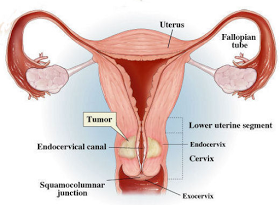
Cervical cancer is a malignant cancer that forms in tissues of the cervix ( the organ connecting the uterus to the vagina ) . There are several types of cervical cancer . The most commonly known type is squamous cell carcinoma ( SCC ) , which is 80 to 85 percent of all cervical cancers . Infection of Human Papilloma Virus ( HPV ) is one of the main factors of this type of cancer growth .
Other types of cervical cancer such as adenocarcinoma , small cell carcinoma , adenosquamous , adenosarcoma , melanoma and lymphoma , a rare type of cervical cancer is not associated with HPV . Some types of cancer that have been mentioned , can not be addressed as SCC .
WHAT are the symptoms?
Early stage cervical cancer are asymptomatic .
See your doctor immediately if you experience symptoms of cervical cancer as follows :
Vaginal Bleeding
* Back pain
* Pain during urination and cloudy urine
* Chronic constipation and feeling bloated although empty stomach .
* Pain during sex and vaginal discharge
* One foot swell
* Leakage of urine or feces from the vagina
Carcinoma in situ ( CIS OR CIN ) .
Carcinoma in situ ( CIN ) is a collection of pre - malignant cancer cells that are in one location and has not moved from its initial position and spread to other body parts . Fortunately in Singapore and other developing countries , the spread of cervical cancer screening programs can reduce cases of invasive cervical cancer .
Pap smears can identify CIN in the cervix , where treatment can prevent the development of cancer . Women are recommended to do a Pap smear at least once a year from the time the woman to have sex , until the age of 70 years . When two of the three of the abnormal Pap smear result , women can reduce the frequency of examination into two to three years. However , women with a high risk level (see below) is recommended to keep doing the inspection once a year.
CIN does not grow at all the women who were infected with HPV , and not all women who have CIN cervical cancer . Such infections in general , many HPV infections heal automatically because the immune system .
However , some specific types of HPV can live in the cervix for many years , changing the genetic makeup of cervical cells , which convert it into dysplasia ( abnormal cell growth ) . Over time , if no action is taken , the more severe dysplasia can and will develop into invasive cervical cancer .
CIN does not show any symptoms . This is why regular cancer screening is a step in the right treatment , because if detected early , CIN can be treated with a chance of complete recovery .
WHAT IS THE CAUSE OF THIS CANCER , AND WHO risk for this disease ?
Infected Human Papilloma Viruses ( HPV ) is the most common cause or a major factor in cervical cancer . These viruses are transmitted through sexual contact , either oral or anal .
Every sexually active women are at risk for cervical cancer . However, women with more than one sex partner have a greater risk . Women who have sex without protection before the age of 16 years have the highest risk level .
Some vaccinations have been developed and effectively kill HPV is the cause of 70 to 85 percent of cervical cancers . The HPV vaccine is intended for girls and women from ages 9 to 26 years because the vaccine only works before infection occurs . However , vaccination can still be performed on women who have not been sexually active in adulthood . The high price of the vaccine is the cause of concern . However , because the vaccine in only for certain types of high-risk cancer , women still have to do a Pap smear , even after vaccination .
You may want to talk with your doctor about your own risk factors and the possible benefits and harms of being screened for lung cancer . Like many other medical decisions , the decision to be screened is a personal one . Your decision may be Easier after learning the pros and cons of screening .
HOW TO DIAGNOSE THE CERVICAL CANCER ?
Although the Pap smear is an effective way as a cervical cancer screening test , diagnostic certainty of the diagnosis of cervical cancer or pre - cancer requires a biopsy of the cervix . A biopsy is generally done through colposcopy , cervical inspection through an enlarged image with dissolving acid to clarify the abnormal cells on the surface of the cervix . This process takes 15 minutes and without causing pain .
Advanced diagnostic procedures include procedures Loop Electrical Excision Procedure ( LEEP ) , cone biopsies and punch biposies .
TREATMENT & CARE
Stage Determination and Treatment of Cervical Cancer
The Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics ( FIGO ) classification of cervical cancer based on the results of the scan into CIN I to III , where CIN III is the initial cause of cervical cancer . On top of CIN III cells means that there has turned into cancer , and will be determined as stage 0 ( where the cancer is still confined to the area of the skin ) to 4B ( which has a spread in other organs ) .
At stage 1 stage , the patient may be given medication through a conservative surgical procedure for women who wish to preserve their fertility , while others are recommended to remove the entire uterus and cervix organ ( trachelectomy ) . After the surgical procedure , it is generally recommended to wait at least one year prior to pregnancy program . Because there is the possibility of the spread of cancer to the lymph nodes when the final stage of stage 1 , the surgeon may lift some lymph nodes from around the uterus for pathology evaluation materials .
Growing the return on the remaining cervical cancer is very rare if the cancer has completely removed through trachelectomy . However , patients are encouraged to remain active prevention and follow-up examination , including Pap smear screening .
Tumors at an early stage can be treated through a procedure of radical hysterectomy ( removal of the uterus ) with removal of lymph nodes . Radiation therapy with or without chemotherapy may be given after a surgical procedure to reduce the risk of cancer returning . Large tumors early age can be treated with radiation therapy and chemotherapy first. Hysterectomy can be done later to control cancer locally better .
Tumor berstadium advanced (stage 2B to 4B ) should be treated with chemo - radiation therapy .
What degree of safety of Cervical Cancer ?
With treatment, the 5 -year survival rate for cervical cancer at an early stage is 92 percent , 80 to 90 percent for stage 1 cancer , and 50 to 65 percent for stage 2 . Only 25 weeks to up to 35 percent of women who are at stage 3 and 15 per cent for those with stage 4 cancer, which managed to survive after 5 years.
Therefore , screening and early detection of cervical cancer is very important .
Thank you for reading this article. Written and posted by Bambang Sunarno. sunarnobambang86@gmail.com
author:
http://schema.org/Personal.
https://plus.google.com/105319704331231770941.
name: Bambang Sunarno.
http://primadonablog.blogspot.com/2014/03/cervical-cancer.html
DatePublished: March 5, 2014 at 19:40
 7MHPNPADAEFW
7MHPNPADAEFWTag : Cervical cancer.
No comments:
Post a Comment