Blood plasma can be separated in a tube containing fresh blood that has been spiked with an anti-coagulant which is then rotated centrifugal until red blood cells fall to the bottom of the tube, white blood cells will be in it and form a layer of buffy coat, blood plasma is above the layer with a density of about 1025 kg / m3, or 1,025 kg / l. Blood serum is plasma without fibrinogen, cells and other coagulation factors. Fibrinogen occupies 4% allocation in the plasma protein and is an important factor in the blood clotting process.
Plasmapheresis is a type of medical therapy that distills (en: extraction) of blood plasma out of the collection of particles for further processing and re-enter the blood plasma at the end of therapy.
Blood Plasma components.
Blood plasma is composed of about 91% water, organic compounds 8%, and 1% inorganic substances. Organic compounds, especially proteins, and plasma is generally described as a colloidal solution of protein in water.Three major plasma proteins are albumin, globulin, and fibrinogen. In 100 milliliters (3.3 oz) of plasma, the approximate concentration of this protein is 4.5 grams (0.16 oz) albumin, 2.5 grams (0.08 oz) globulin, and 0.3 grams (0.01 oz) fibrinogen.
Albumin.
One of the smallest of molecules of protein, albumin has a net electric charge relatively high which makes it possible to deploy around three quarters of the colloid osmotic pressure that is present in the blood stream. It is mostly this pressure that makes a constant volume of blood plasma. Albumin is produced in the liver, and in people with severe liver disease there is a decrease in the amount of albumin in the blood, a condition known as hypoalbuminemia. The amount of albumin can also be reduced by deficiencies in the diet; loss through the urine in some kidney diseases, such as nephrosis; and with prolonged infections, such as osteomyelitis. If the shortage of albumin cause drop in blood pressure, plasma can seep slowly out of the bloodstream and into the tissues of the body. This leads to a condition known as edema, or dropsy, where tissue becomes swollen with excess fluid.Globulin.
There are several types of plasma globulin, and with a technique called electrophoresis small proteins can be separated into fractions known as alpha, beta, and gamma. Alpha and beta globulins perform a variety of functions, including transporting food proteins and other substances by while combining with them. Gamma globulin plays a major role in defending the body against infection, because they bring many antibodies that provide immunity against bacteria and other organisms. If a person is born without the normal amount of gamma globulin, blood can not produce enough antibodies to fight infection.Fibrinogen.
Fibrinogen name literally means "producing fiber," and in the final step of blood coagulation, fibrinogen is converted to fibrin molecules, protein threads that help form clots. Fibrinogen is produced in the liver, and if the amount of fibrinogen in the blood is used too quickly, disturbances known. as a result defibrination.Other Plasma components. In addition to protein, plasma containing other organic substances. Some, such as urea, uric acid, creatinine, and amino acids, is a nitrogen compound. Others, including glucose, neutral fat and cholesterol, which nonnitrogenous.
The main inorganic substances in plasma are electrolytes, including sodium, potassium, chloride, calcium, phosphate, sulfate, and magnesium. When carbon dioxide is released by cells of the body taken up by the blood, mostly done in the plasma in the form of sodium bicarbonate. Minute traces of hormones, vitamins, and enzymes are also present in the plasma.
Differences And Blood Plasma.
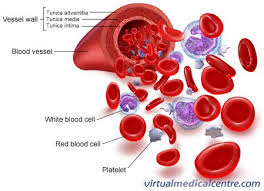
Blood is a liquid that is pushed out by the heart. Blood traveling in various parts of the body through arteries and capillaries, and returns to the heart through the veins. System responsible for transporting blood in the body is the circulatory system. Blood contains substances such as minerals, protein and nutrients needed for the development of cells, tissues and organs. It is said that the blood is the food of the body's systems. The adult male has about 5-6 liters of blood, and an adult woman has about 4-5 liters of blood. Children have about three liters of blood in their body.Blood is also a transport that carries oxygen (O2) through the body and remove carbon dioxide (CO2), and other waste products from the body. Blood when taken from a person, considered as whole blood. Blood has three components, which include red blood cells (erythrocytes), white blood cells (WBCs), plasma, and platelets. These components are usually separated for use in transfusions. Blood is not very often used entirely for the transfusion process; with the exception of cardiac surgery and sickle cell disease, where there is a large amount of blood loss. In addition to nutrition brings, it also brings the immune response, and serves as a heat distributor for the body. Red blood cells from the blood takes longer to fill, about 3 to 5 weeks, and contain antigens that can harm someone's life if the blood donor and the recipient are not compatible, when transfused. Blood is vital for survival.
Plasma is usually cited as a substance that remains behind in the blood when red blood cells are taken out. It is part of a yellow liquid, from whole blood, which makes up 55 percent of whole blood, and it is about 90 percent water. As a major component of blood, is more widely used plasma for transfusion, especially for victims of burns, trauma, and those who suffer from physiological destruction. Plasma contains clotting factors that impede the flow of excessive blood from an open wound. Patients who suffer from hemophilia often transfused with plasma.
Because it can be recharged faster than erythrocytes (approximately within 24 hours), plasma can be donated up to twice a week. One of the processes that are used to treat some autoimmune diseases, is plasmapheresis, or plasma exchange. This is a procedure in which blood is cleaned for therapeutic purposes. It is safer to donate plasma, because it has antibodies that fight infection and harmful substances. Antibodies in the plasma rapidly changed, so that is conducive to donate when the donor and recipient matching. Plasma can be extracted and stored in the freezer for a year. When taken out and thawed, it is called Plasma Fresh, and a small portion coming apart after frozen and thawed, called cryoprecipitate.
Summary :
Blood is drawn from the very substance of the body, while the plasma is one of the blood components.Whole blood is used for patients with sickle cell anemia, and those undergoing heart surgery, while the plasma is usually used for hemophiliacs, or burns, trauma and the patient unconscious.
Plasma is safe for transfusion if there may be a risk of incompatibility.
Plasma can be recharged faster than erythrocytes.
Plasma contains clotting factors to stop bleeding.
Thank you for reading this article. Written and posted by Bambang Sunarno. sunarnobambang86@gmail.com
author:
https://plus.google.com/105319704331231770941.
name: Bambang Sunarno.
http://primadonablog.blogspot.com/2015/09/about-blood-plasma.html
DatePublished: 11 September 2015 at 09:05
Tag : Blood Plasma.
Code : 7MHPNPADAEFW


No comments:
Post a Comment